A W-2 form, officially known as the Wage and Tax Statement, serves as an essential document issued by employers in the United States to report an employee’s annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. This form is a crucial component of the annual tax filing process for employees, providing the necessary information to accurately complete their tax returns.
Employers must send out the W-2 form to their employees by January 31st each year, ensuring that employees have ample time to file their taxes by the April deadline. The information on a W-2 includes wages earned, federal and state taxes withheld, Social Security and Medicare contributions, and any other deductible or deferred compensation.
What is the W2 Form?
The W-2 form, officially known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is an essential document used in the United States to report an employee’s annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. It is issued by employers to every employee from whom income, social security, or Medicare tax was withheld during the year.
Key Information on a W-2 Form Includes
- Employee’s earnings for the year (including wages, tips, and other compensation).
- Federal income tax withheld, showing how much tax the employer sent to the IRS on the employee’s behalf.
- State and local taxes withheld, if applicable.
- Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld, as these are part of the FICA (Federal Insurance Contributions Act) taxes.
- Contributions to retirement plans, such as a 401(k).
- Other benefits and deductions, including health insurance premiums and dependent care benefits.
Distribution
Employers are legally required to send the W-2 forms to their employees by January 31st each year, ensuring that employees have enough time to file their taxes before the deadline (typically April 15th). Employers also send copies to the Social Security Administration to report earnings.
For employees, this form is crucial because it provides the necessary information to ensure their tax returns are complete and accurate, helping to determine if they owe additional taxes or are due for a refund.
What is a W2 Form Used For?
The W-2 form is used primarily for the following purposes in the United States:
- Tax Filing: It provides detailed information about an employee’s annual wages and the taxes withheld from those earnings. This includes federal income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, and any applicable state and local taxes. Employees use this information to complete their annual federal and state tax returns.
- Income Verification: The W-2 form serves as an official document to verify an employee’s income. This is often required when applying for loans, mortgages, or other forms of credit. It may also be needed for applications for housing, government assistance, or other needs that require proof of income.
- Social Security Benefits: The information on the W-2 form helps the Social Security Administration (SSA) track an individual’s earnings history. This data is crucial for calculating Social Security benefits upon retirement, disability, or for survivor benefits.
- Healthcare and Other Benefits: Information on the W-2 can include contributions to retirement plans (like a 401(k)), health insurance premiums paid, and other benefit-related deductions. This helps both employees and the IRS ensure that proper contributions are being made and that tax advantages are correctly applied.
The W-2 form is a critical component of the annual tax and income documentation process in the U.S., helping both taxpayers and the government ensure accurate financial records and tax compliance.
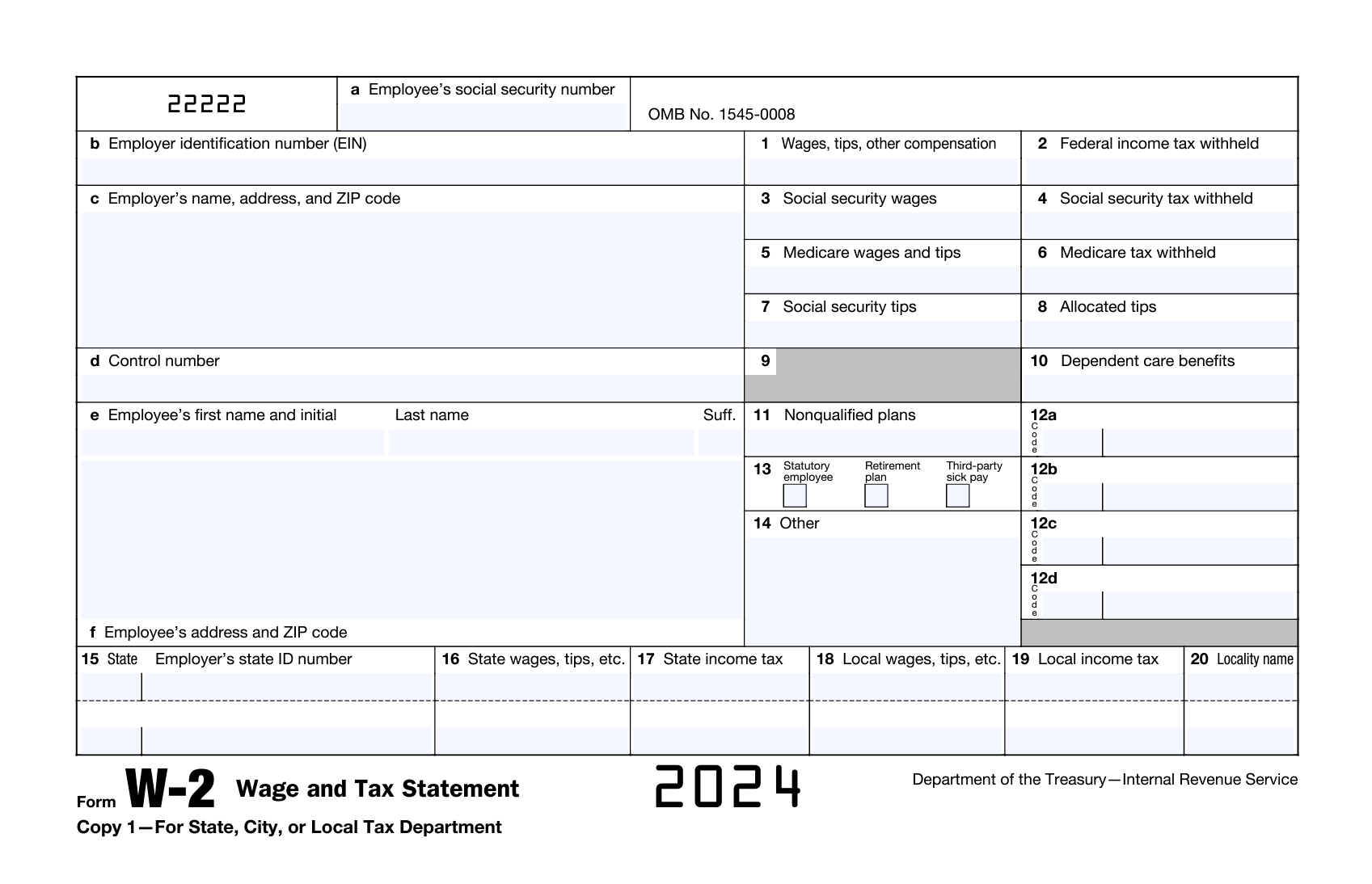
Decoding W-2 Form Boxes
The W-2 Form is divided into three sections, as follows:
Section A-F: Employee and Employer Information
The first section begins with critical identification information for both the employee and employer:
- Box a. Employee’s Social Security Number: This is a crucial identifier used for tracking Social Security benefits and for tax reporting purposes.
- Box b. Employer Identification Number (EIN): Assigned by the IRS, this unique number identifies the taxpayer (employer).
- Box c. Employer’s Name, Address, and ZIP Code: Lists the official name and address of the employer.
- Box d. Control Number: An optional identifier that helps employers differentiate between multiple W-2 forms in their records.
- Box e. Employee’s Name and Address: Displays the full name and current address of the employee.
- Box f. Employee’s Address and ZIP Code: Provides a detailed address for sending correspondence.
Section 1-14: Financial and Tax Information
The second section details the financial and tax-related information relevant to the employee:
- Box 1. Wages, Tips, Other Compensation: The total of all taxable wages, tips, and other compensation like bonuses received by the employee.
- Box 2. Federal Income Tax Withheld: The amount of federal tax that has been withheld from the employee’s paycheck throughout the year.
- Box 3. Social Security Wages: The earnings that were subject to Social Security tax, which may differ from the total wages due to specific caps and exclusions.
- Box 4. Social Security Tax Withheld: The actual amount of Social Security tax deducted from the employee’s earnings.
- Box 5. Medicare Wages and Tips: Total earnings that were subject to Medicare tax.
- Box 6. Medicare Tax Withheld: How much Medicare tax was taken from the employee’s earnings.
- Box 7. Social Security Tips: The total amount of tips reported to the employer that are subject to Social Security taxes.
- Box 8. Allocated Tips: Tips allocated to the employee by the employer, not included in the usual taxable wages.
- Box 9. Blank: This box is now obsolete and no longer used.
- Box 10. Dependent Care Benefits: The amount of dependent care benefits received under a section 129 dependent care plan, which might be exempt from taxation.
- Box 11. Nonqualified Plans: The distributions from non-qualified deferred compensation plans or nongovernmental section 457 pension plans.
- Box 12a-d. Code: These boxes include various codes that report additional compensations and benefits, such as retirement plan contributions and insurance premiums.
- Box 13. Checkboxes for Statutory Employee, Retirement Plan, Third-Party Sick Pay: Indicates specific employment statuses such as statutory employee, participation in a retirement plan, or receipt of third-party sick pay.
- Box 14. Other: Captures any additional tax information not included elsewhere, such as union dues or post-tax health insurance premiums paid.
Section 15-20: State and Local Tax Information
This third section reports state and local tax details:
- Box 15. State & Employer’s State ID Number: Identifies the state of employment along with the employer’s state tax ID number.
- Box 16. State Wages, Tips, etc.: The total earnings subject to state taxes.
- Box 17. State Income Tax: The total state income taxes withheld from the employee’s earnings.
- 18. Local Wages, Tips, etc.: The earnings subject to local, city, or other local taxes.
- 19. Local Income Tax: The total local taxes withheld.
- 20. Locality Name: The specific locality (city, county) that is taxing the earnings.
Can You Print a W2 Form?
Yes, you can print a W-2 form, but there are specific guidelines and requirements you need to follow if you are an employer providing these forms to employees:
- IRS-Approved Forms: Employers must use W-2 forms that are approved by the IRS for printing. These forms are scannable by the IRS systems. You can order these forms from the IRS, purchase them from office supply stores, or use payroll software that supports IRS-approved W-2 printouts.
- Black Ink: The form must be printed in black ink to ensure it is readable by both humans and IRS scanning systems.
- Legibility: Ensure that the printout is clear and legible. Poor quality printouts can cause processing delays or errors.
- Employee Copies: Employers need to provide multiple copies of the W-2 to employees:
- Copy A: To be filed with the employee’s federal tax return (unless filing electronically).
- Copy B: To be filed with the employee’s state, city, or local tax return (if applicable).
- Copy C: For the employee’s records.
- Additional copies may be needed for local tax filings depending on the employee’s location.
- Print on Correct Paper: If you are printing copies of the W-2 form for submission to the Social Security Administration (Copy A), it must be printed on a specific type of paper that meets the SSA’s requirements for machine readability.
- Electronic Delivery: If your employees agree, you can also distribute W-2 forms electronically, which employees can then print if they choose. This method requires consent from the employee to receive forms in a digital format.
For employees, if you receive a digital copy of your W-2 form (via email or through an employer portal), you can print it on standard white paper for your records or to attach to your tax return if you are filing by mail. Ensure that your personal printer settings produce a clear and legible document.
Obtaining and Printing W-2 Form Printable
To obtain and print a W-2 form, follow these guidelines:
If You’re an Employer
- Official Forms: Employers must use official W-2 forms from the IRS for their employees. These forms are scannable and designed to meet IRS requirements. You can order these forms for free from the IRS website or pick them up from an IRS office. Some office supply stores also sell IRS-approved W-2 forms.
- Printing Requirements: Make sure you use a printer that can produce clear and legible documents. The IRS requires that these forms be printed in black ink so they can be read by their scanning equipment.
- Multiple Copies: You will need to print multiple copies of the W-2 form for each employee:
-
- Copy A: Sent to the Social Security Administration (SSA).
- Copy B: Given to the employee for their federal tax return.
- Copy C: Kept by the employee for their records.
- Copy D: Kept by the employer as a record.
- Additional copies may be needed for state or local tax departments, depending on your location.
If You’re an Employee
- Digital Copies: If your employer provides electronic access to your W-2 (commonly through an online employee portal), you can download and print the form from there. Make sure you have a PDF reader installed on your computer, as most W-2 forms are provided in PDF format.
- Print from Home: Once you have the file, open it using a PDF reader, and use your home printer to print the form. Check your printer settings to ensure the printout is clear and legible, as you’ll need it for your tax records and possibly for other official purposes.
- Public Services: If you don’t have a printer at home, you can use local printing services at places like public libraries, office supply stores, or print shops.
These steps should help you access and print your W-2 form easily, whether you are an employer or an employee.
Blank W2 Form 2025 Download
As of now, the W-2 form for the year 2025 isn’t available. The IRS typically updates and releases forms for a specific tax year towards the end of that year or at the beginning of the next year. For instance, W-2 forms for the year 2025 will likely be available by late 2024 or early 2025.
Here are some ways to access and download the W-2 form once it becomes available:
- IRS Website: The IRS regularly updates its forms and publications on its official website. You can download the W-2 form for 2025 from there once it’s released.
- Employer’s Payroll or HR Portal: Many employers provide W-2 forms electronically through their internal HR or payroll systems. You can download the form directly from there when it’s available.
- Tax Filing Software: Platforms like TurboTax, H&R Block, and others typically provide updated tax forms as part of their tax preparation software. If you use such a service, you can access the W-2 form directly through the software.
To ensure you have the correct and most up-to-date version of the W-2 form when you need it, keep checking the IRS website or your employer’s communication as the end of the tax year approaches.
Can You Get W2 Form Online?
Yes, you can obtain your W-2 form online in several ways:
- Employer’s Payroll or HR Portal
- Tax Filing Services
- IRS’s Get Transcript Tool
How to Get a W-2 file?
To obtain your W-2 form, you can follow these steps:
- From Your Employer: The easiest way to get your W-2 form is directly from your employer. Employers are required to provide you with your W-2 form by January 31st. If you haven’t received it by this date, contact your employer’s payroll or human resources department to request a copy.
- Electronically: Many employers offer the option to receive your W-2 electronically. This is often done through a secure portal where you can access and print your W-2 as needed. Check with your employer to see if they offer this option and how you can sign up for it.
- IRS Request: If you can’t obtain your W-2 from your employer or if the employer has gone out of business and you have not received your W-2 by the end of February, you can contact the IRS for assistance at 1-800-829-1040. You will need to provide your personal information, including your Social Security number and the dates of your employment. The IRS will attempt to contact your employer on your behalf.
- IRS Form 4852: If you still cannot obtain your W-2, you can use IRS Form 4852, “Substitute for Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement.” This form allows you to estimate your wage and tax withholding as accurately as possible. However, using this form could delay your refund and may require correction if the estimated data differs from the actual data reported by your employer.
- Previous Tax Preparer: If you used a tax preparer or software in previous years, you might be able to access past years’ W-2s if they were saved or stored with your tax records.
Always keep your address updated with your current and past employers to ensure that you receive your W-2 forms without any issues.
Where Can You Get Your W2 Form?
To obtain your W-2 form, you have several options:
- From Your Employer: Typically, your employer is your primary source for your W-2 form. Employers are required to send out W-2 forms to employees by January 31st each year. If you haven’t received it by this date, contact your employer’s payroll or human resources department to inquire about it.
- Employer’s Online Portal: Many companies provide their employees access to an online portal where W-2 forms can be viewed and downloaded. Check if your employer offers such a portal, and ensure you are registered to use it.
- IRS Assistance: If you cannot obtain your W-2 from your employer or if there are issues such as the company closing down, you can contact the IRS for help. After February 14, you can call the IRS at 1-800-829-1040. You will need to provide your personal details, employer’s information, and an estimate of your earnings and taxes withheld. The IRS may then contact your employer on your behalf to request the missing form.
- IRS Get Transcript Tool: You can use the IRS Get Transcript tool to obtain a transcript of your W-2. This transcript provides a summary of your W-2 information but is not an actual copy of the W-2 form. It’s useful for tax filing if you cannot get the actual form in time. You can access this tool through the IRS website.
Ensure that your contact information is up to date with your current and previous employers to avoid delays in receiving your W-2 form